Note Taking.
http://owll.massey.ac.nz/study-skills/note-taking-methods.php
There are a number of different ways to take notes, and it is best that you use the method you feel most at ease with. However, there are four general ideas that could help you to improve your note taking:
- Use white space to separate major ideas.
- Try to limit your notes to one concept or section per page.
- Use abbreviations and/or symbols where possible to avoid long sentences.
- Write down the information in your own words.
Cornell Method.
The Cornell Method is based on two columns: one containing the keyword or concept, and the other containing the description or notes associated with the keyword or concept. This method can be used while listening to the lecturer. In the right hand column, you can list the main ideas or write a paragraph and then on the left hand side note the keyword or concept that relates to your section of notes. At the bottom of the page you should write paragraphs summarising the information contained in the notes

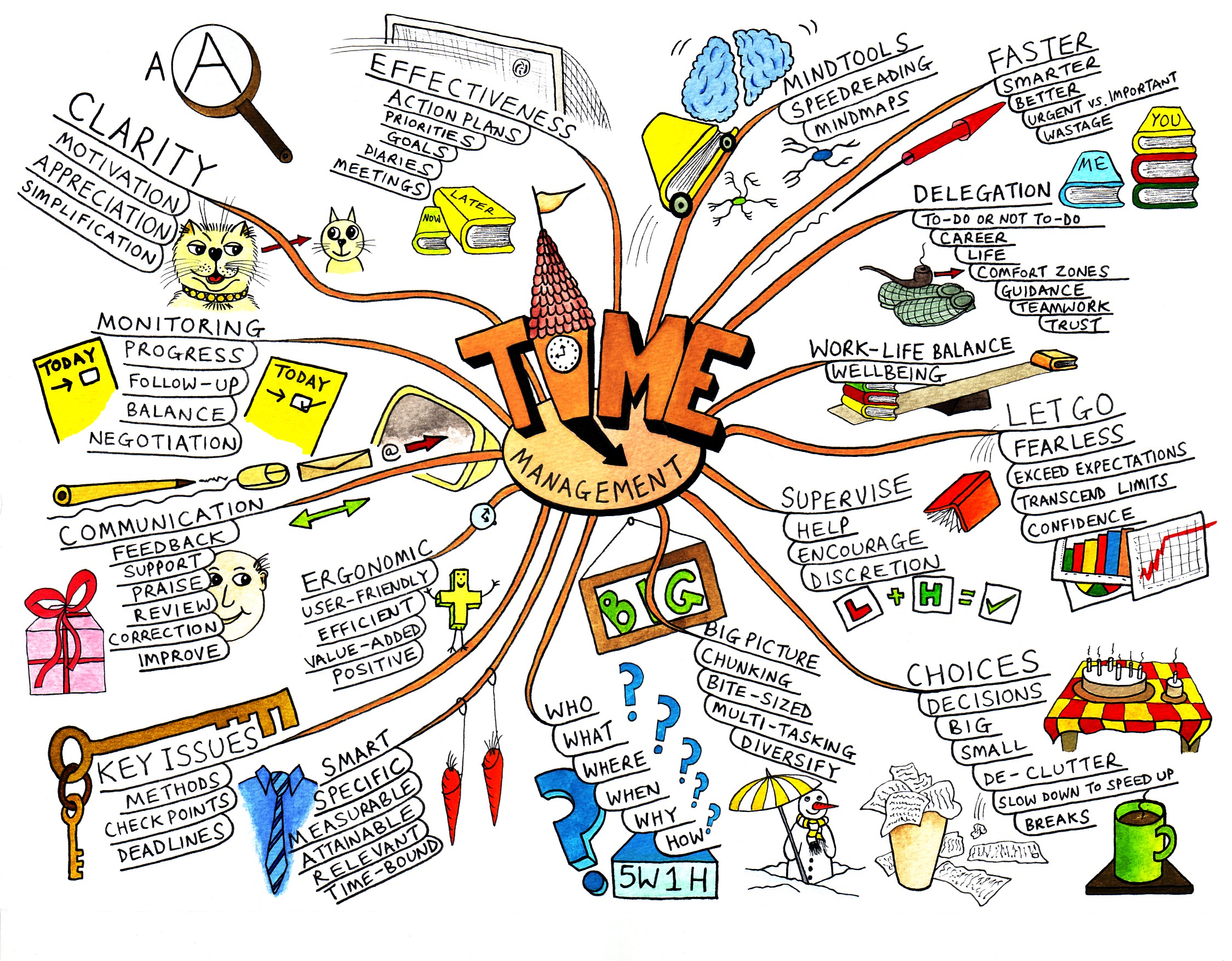
Mind Map
A mind map is a diagram in which ideas, concepts and images are linked together around a central concept, keyword or idea.
The outlining method
This method involves writing a series of topics and sub-topics, and identifying them by indenting the text, numbering the lines, or using a dash or bullet point.
- Main Topic
- Sub-Topic
- Detailed points
- Detailed points
- Sub-Topic
- Second Main Topic
The Sentence Method
With this method you simply write every new concept, or topic on a separate line. You can also number the information if you wish. It is recommended that you use some form of visual aid to group related points together.


